Social media have been developed as a great point where people communicate with their interested people, share thoughts and opinions, reflect their moods, feelings, and sentiments. Taking advantage of this, Research has been done several years ago which we will be analyzing here,
Link to the research paper 👉 Click Here
The aim is to analyze Facebook data to detect any factors that may reflect the depression of relevant Facebook users. Various machine learning techniques are employed for such purpose.
Considering the key objective of this study, the following are subsequent research challenges addressed in paper.
Define what depression is and what are the common factors contributing to depression.
What are the factors to look for depression detection in Facebook comments?
How to extract these factors from Facebook comments?
What is the relationship between these factors and attitudes toward depression?
When is the most influential time to communicate within depressive Indicative Facebook users?
What are the most influential machine learning techniques for the detection of depression in Facebook comments?
There are various other researches which are based on Depression detection authors have mentioned them in research paper.
Research
First focused on four types of factors such as emotional process, temporal process, linguistic style and all (emotional, temporal, linguistic style) features together for the detection and processing of depressive data received as Facebook posts.
We then apply supervised machine learning approaches to study each factor types independently. The classification techniques such as ‘decision tree’, ‘k-Nearest Neighbor’, ‘Support Vector Machine’, and ‘ensemble’.
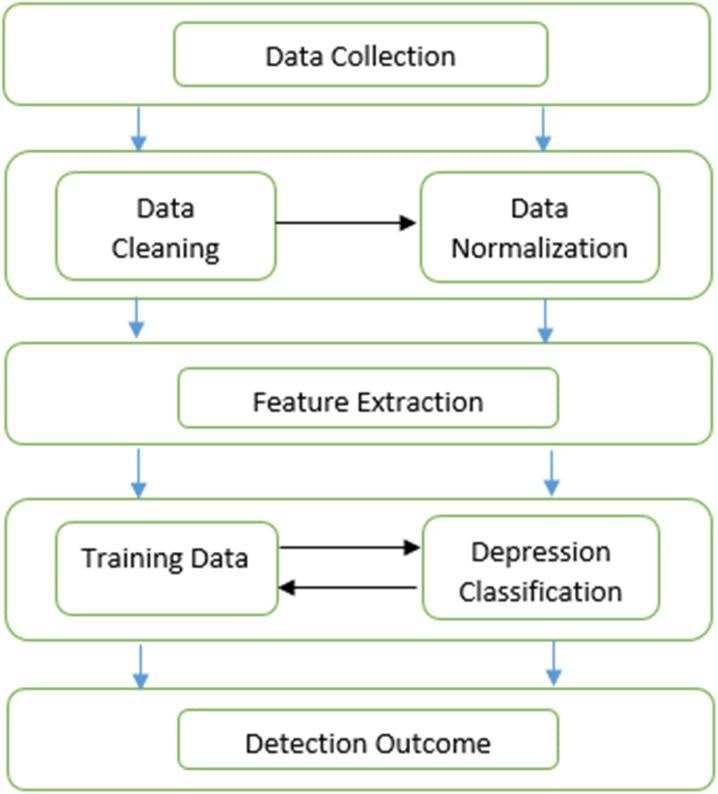
Dataset Exploration
In particular, Facebook user’s comments are one of the primary challenges which bear information on whether or not they could contain depression-bearing content.
To tackle this issue using NCapture for collecting data from Facebook can make it easy.
NCapture is intended to enable to arrange, break down and discover knowledge in unstructured data like open-ended survey responses, social media, interviews, articles and web content. Furthermore it gives a place to arrange and deal with material to discover knowledge in a more proficient way.
Dataset Preparation
After collecting the raw data from Facebook, it was analyzed by using LIWC package.
LIWC is the Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count library of Python. The primary dataset contained total 21 columns where 13 columns represent the linguistic style (articles, prepositions, auxiliary verbs, conjunctions, personal pronoun, impersonal pronouns, verbs, negation, etc.) information, 5 columns represent the emotional (positive, negative, sad, anger and anxiety) information, 3 columns represent the temporal process (past, present and future) information and each column gives the individual information’s about depressive behavior .
Labeling
The Facebook data containing users’ comments were divided into two sets
(a) for the positive (YES) class (depression indicative comments) and
(b) for the negative (NO) class (non-depression indicative comments).
Feature Extraction
To describe and demonstrate amongst depressive and non-depressive posts, different features were extracted in view of psycholinguistic measurements from the user’s post.
Psycholinguistic features LIWC is a psycholinguistic vocabulary package made by psychological analysts to perceive the different affective, intellectual, and etymological parts lies on user’s verbal or written correspondence. It returns more than 70 different factors with higher level of psycholinguistic features, for example,
- Psychological process—affective process, social process, cognitive process, perceptual process, biological process, drives, time orientations, relativity, personal concerns
- Linguistic process—word count, word/sentence, pronoun, personal pronoun, articles, prepositions, auxiliary verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, Negations
- Others grammar—verbs, adjectives, comparisons, interrogatives, number, quantifiers.
These higher-level categories are also divided into subcategories such as
- Biological processes—sexual, body, ingestion and health
- Affective processes—anxiety, anger, sadness, positive emotion, negative emotion
- Time orientations—present, past, future
- Social processes—family, friends, male, female
- Perceptual processes—see, hear, feel.
In this research work, only 23 among 70 factors are taken and changed over every depressive and non-depressive post into numerical values in view of psycholinguistic features.
Measuring depressive behavior
A set of attributes like emotional process, temporal process, and linguistic style can be used to characterize the depressive behaviors of users.
Dataset consists of five emotional variables (positive, negative, sad, anger, anxiety), three temporal categories (present focus, past focus, and future focus), and 9 standard linguistic dimensions (e.g., articles, prepositions, auxiliary verb, adverbs, conjunctions, pronoun, verbs, and negations).
Emotional Process:
The analysis of the emotional comments of social network data can be leveraged to produce reliable predicts in a variety of circumstances.
Psycholinguistic dimensions were used for considering five features of the emotion state manifested in the comments: positive affect (PA), negative affect (NA), sadness affect (SA), anger affect (AA), and anxiety affect (AnA)
Temporal Process:
Generally, temporal process word provides information about past focus category, present focus category, and future focus category of how people are referencing each other and their degree of emotionality.
Linguistic Process:
The linguistics process is one of the largest parts of the LIWC psycholinguistics vocabulary package.
It has been effectively used to recognize connections between people in social co-operations, including relative status, trickiness, and the nature of close relationships.
So, In this study nine specific linguistics features (articles, prepositions, auxiliary verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, personal pronouns, impersonal pronouns, verbs, and negations) to characterize user comments for our experimental analysis.
Classification Model:
This stage constructs a prediction model for depression post/comments recognition, by considering the psycholinguistic features as input.
In this work, four popular classifiers were used: Support Vector Machine (SVM), Decision Tree, Ensemble, and k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN).
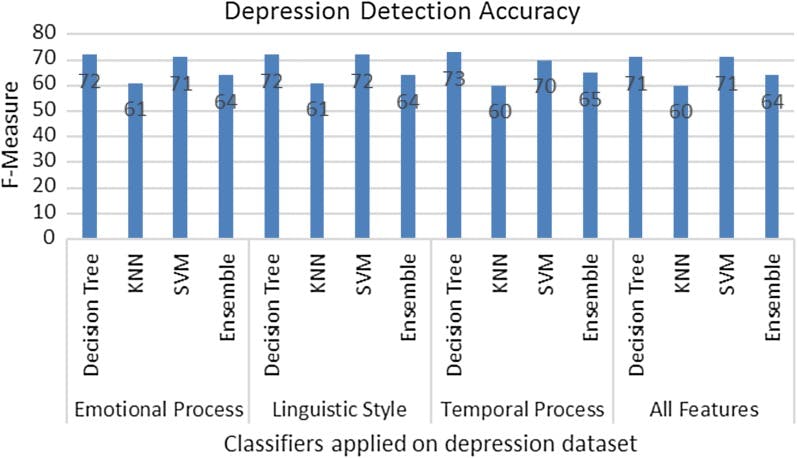
The outcome shows that the best performing model is Decision Tree. Here, for temporal process and all features, KNN and SVM give almost same the high precision but Decision Tree gives the highest result for Recall and F-measure relating to the class of depression indicative comments of Facebook users.
Time-series Analysis:
Time series is a record of phenomenon unpredictably fluctuating with time is called time series and Time-series data is a kind of fleeting information which is normally high dimensional and large in data size.
Here we focus on understanding the time patterns(HH:MM:SS) of Facebook users, at AM (00:00:01 –11:59:59) and PM (12:00:01 – 23:59:59).
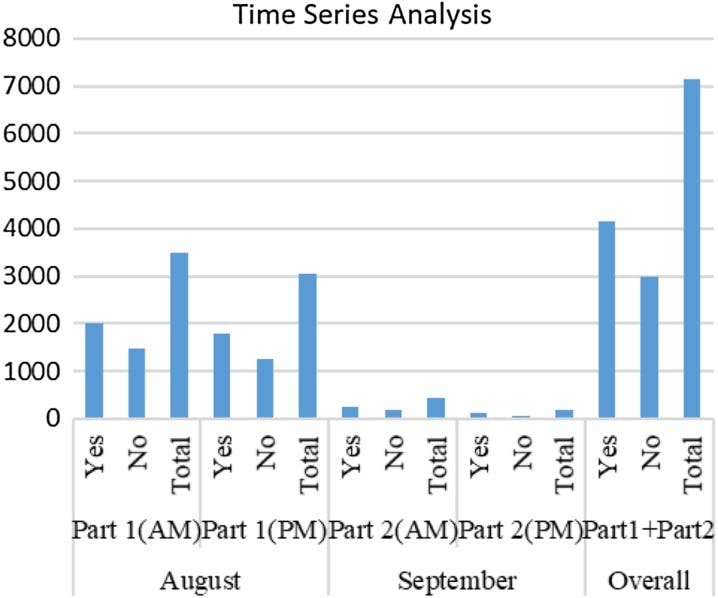
We observe the monthly depression pattern. It is showing that we have a total 7146 number of comments. 91.14% samples of comments ranging between August 01, 2017–August 30, 2017, and 8.85% between September 01, 2017–September 09, 2017.
We observed that the hourly depression patterns with the highest rate in AM. We also observed that the monthly depression pattern shows a seasonal trend, with the highest depression observed during both August and September in the AM, while the lowest during both August and September in the PM.
In summary, we view persistent rhythms in depression expression on social media throughout multi-day crosswise over people. This provides us with a promising mechanism to monitor fine-grained temporal trends of depression across populations and regions.
Conclusion
There are three types of factors (emotional process, temporal process, linguistic style) and trained a model to utilize each type of factor independently and jointly. We use machine learning techniques to classify the features of comments. Findings showed that all of the results of the classifiers are almost between 60 and 80%.